MVC Application
You can initiate the project through Spring Initializr
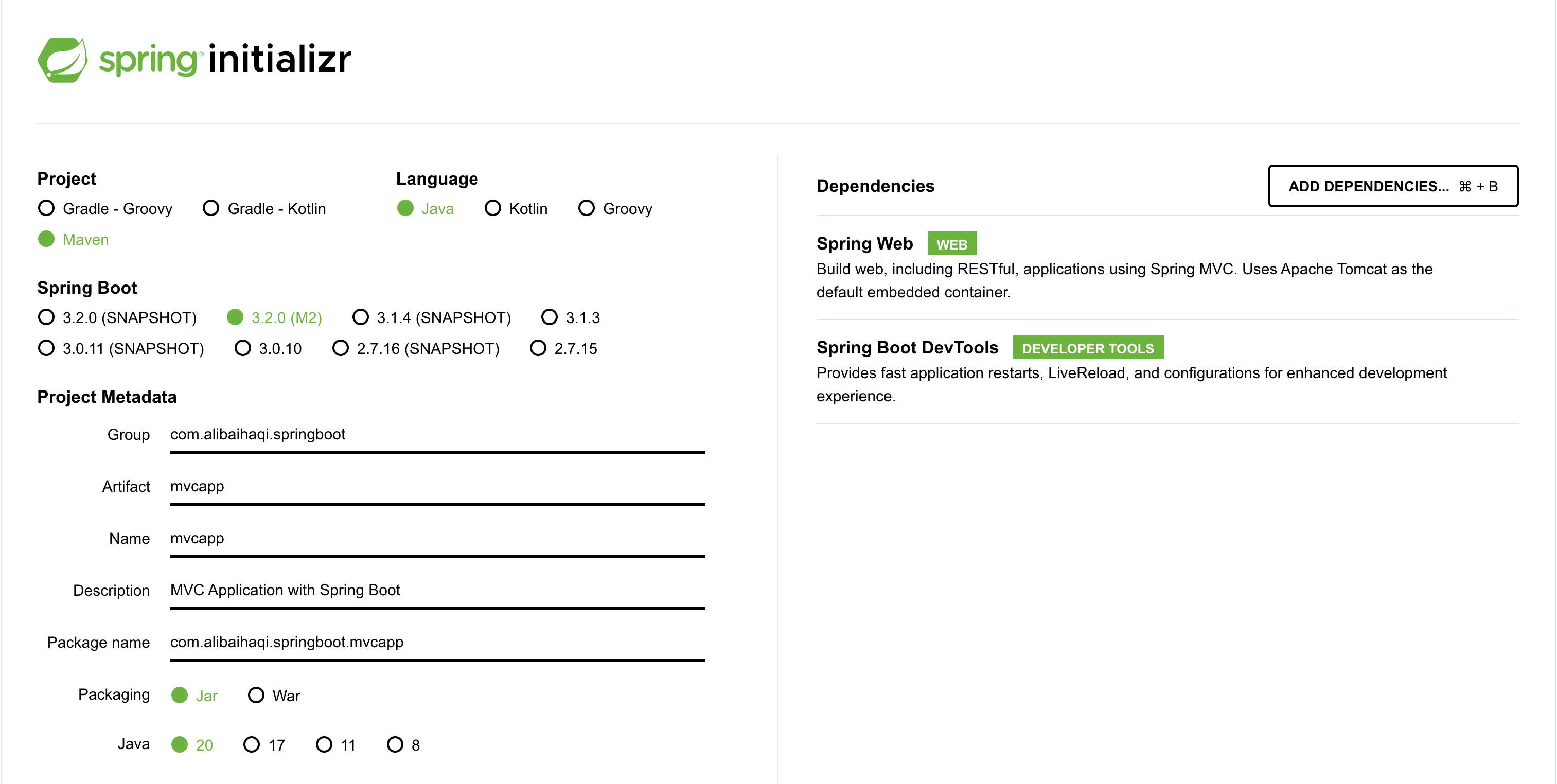
This application will use:
- Project:
Maven - Programming Langauge:
Java - Spring Boot:
3.2.0(M3)-> It's recommended to use stable version, but you still can useSNAPSHOT(it's version under development or experimental probably). - Dependencies:
Spring Web: to enable build Web, RESTful API, and Apache Tomcat as an default embedded containerSpring Boot DevTools: to enable hot reload the application without kill the application (you might need some configuration in different text editor)Spring Boot Starter Test: to enable integration with Java Test
First Common APIs
package com.alibaihaqi.springboot.mvcapp.common;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class CommonController {
@RequestMapping("common")
@ResponseBody
public String commonResponse() {
return "Hello!";
}
}Generate simple HTML file
You can use StringBuffer to generate the HTML but it really painful by append it one-by-one.
[With StringBuffer]
package com.alibaihaqi.springboot.mvcapp.common;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class CommonController {
@RequestMapping("common-html")
@ResponseBody
public String commonHtmlResponse() {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
sb.append("<html>");
sb.append("<head>");
sb.append("<title>MVC App</title>");
sb.append("</head>");
sb.append("<body>");
sb.append("<p>My MVC App</p>");
sb.append("</body>");
sb.append("</html>");
return sb.toString();
}
}Use Apache Tomcat Embed
By using Apache Tomcat Embed package, you can move your HTML file as an independent page.
You can setup by install the dependency through pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>Add the prefix and suffix information as a relative path for asset locations
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/WEB-INF/jsp/
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jspAdd your first JSP file, for example your file on this path /src/main/resources/META-INF/resources/WEB-INF/jsp/commonJsp.jsp
<html>
<head>
<title>MVC App</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>My MVC App</p>
</body>
</html>Implement it on your Controller
package com.alibaihaqi.springboot.mvcapp.common;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class CommonController {
// We remove @ResponseBody to indicate the Spring Boot
// that we want to serve other resources, such as JSP file
// commonJsp will refer as the view name
@RequestMapping("common-jsp")
public String commonJspResponse() {
return "commonJsp";
}
}Query Parameters
In the browser, you can add query param in the end of the URL page. For example, http://www.example.com/somepage?d=20231018 where http://www.example.com/somepage is the page you want to access, and d=20231018 is the query param append to the URL.
You need to specifically input in the controller of the page.
@Controller
public class LoginController {
// Use Logger instead of System.out.println or else in Production
// So, we can control from application.properties which level should be printed in the development
// and production
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@RequestMapping("login")
// In this case, you want to explicitly tell the page that you require the page to add param `name` in the URL
// or you will give the response 400
public String loginPage (@RequestParam String name, ModelMap model) {
System.out.println("Request param is " + name); // NOT RECOMMENDED FOR PRODUCTION
logger.debug("Request param is {}", name);
// You want to inject the param to the HTML page
model.put("name", name);
return "loginJsp";
}
}@Controller
public class LoginController {
// Use Logger instead of System.out.println or else in Production
// So, we can control from application.properties which level should be printed in the development
// and production
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@RequestMapping("login")
// In this case, you will process some logic if query params appear in the URL
public String loginPage (@RequestParam(required=false) String name, ModelMap model) {
System.out.println("Request param is " + name); // NOT RECOMMENDED FOR PRODUCTION
logger.debug("Request param is {}", name);
// You want to inject the param to the HTML page (if available)
model.put("name", name);
return "loginJsp";
}
}Here is the example when you put the required param in the code but the param is missing.

For logging, Spring Boot Starter Web is already included logging dependency called spring-boot-starter-logging with default Logback with SLF4j